On May 28, 1830, Congress passed the Indian Removal Act, beginning the forced relocation of thousands of Native Americans in what became known as the Trail of Tears. Not all members of Congress supported the Indian Removal Act. Tennessee Rep. Davey Crockett was a vocal opponent, for instance. Native Americans opposed removal from their ancestral lands, resulting in a long series of battles with local white settlers. But the forced relocation proved popular with voters. It freed more than 25 million acres of fertile, lucrative farmland to mostly white settlement in Georgia, Florida, North Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, and Arkansas. More than 46,000 Native Americans were forced—sometimes by the U.S. military—to abandon their homes and relocate to “Indian Territory” that eventually became the state of Oklahoma. More than 4,000 died on the journey—of disease, starvation, and exposure to extreme weather.
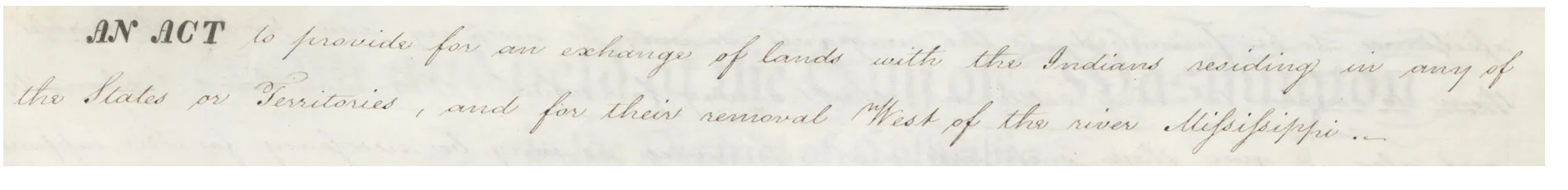

The Indian Removal Act, May 28, 1830. General Records of the United States Government, National Archives.
